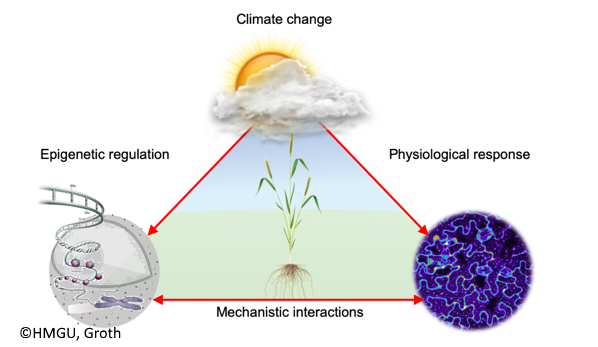
Chromatin modifications, such as DNA and histone methylation, depend on metabolic intermediates as cofactors used by the chromatin modifying enzymes. Plants undergo extensive metabolic changes between day and night, but the resulting implications for chromatin modification and epigenetic regulation are not well understood. The project aims to describe new mechanisms linking diurnal dynamics of one-carbon metabolism and epigenetic regulation. For this, interdisciplinary approaches including genetics, state-of-the art omics technologies and facilities for environmental simulation and phenotyping will be used to characterize environment-dependent diurnal physiological changes, metabolic profiles, and chromatin modification patterns in Arabidopsis thaliana wild-type and mutant lines. Metabolic fluxes will be quantified by isotope labeling to determine the involved dynamics. Cellular regulatory networks will be analyzed using protein interaction and localization experiments. Ultimately, our goal is to pinpoint key regulatory pathways involved in plant-environment interaction, which will help to predict and manage to effects of climate change on plants as the foundation of food security and health.
Related literature
- Harris CJ et al. (2018). A DNA methylation reader complex that enhances gene transcription. Science, 362(6419):1182.
- Liu W et al. (2018). RNA-directed DNA methylation involves co-transcriptional small-RNA-guided slicing of polymerase V transcripts in Arabidopsis. Nature Plants, 4(3):181-8.
- Groth M et al. (2016). MTHFD1 controls DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Nature Commun, 7:11640.
- Groth M et al. (2014). SNF2 chromatin remodeler-family proteins FRG1 and -2 are required for RNA-directed DNA methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111:17666-17671.
- Du J et al. (2014). Mechanism of DNA methylation-directed histone methylation by KRYPTONITE. Molecular Cell 55, 495-504.
- Yelagandula R (2014). The histone variant H2A.W defines heterochromatin and promotes chromatin condensation in Arabidopsis. Cell 158, 98-109.
